Publications
Discovering Favorite Views of Popular Places with Iconoid Shift
In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm for automatic landmark building discovery in large, unstructured image collections. In contrast to other approaches which aim at a hard clustering, we regard the task as a mode estimation problem. Our algorithm searches for local attractors in the image distribution that have a maximal mutual homography overlap with the images in their neighborhood. Those attractors correspond to central, iconic views of single objects or buildings, which we efficiently extract using a medoid shift search with a novel distance measure. We propose efficient algorithms for performing this search. Most importantly, our approach performs only an efficient local exploration of the matching graph that makes it applicable for large-scale analysis of photo collections. We show experimental results validating our approach on a dataset of 500k images of the inner city of Paris.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/iccv/WeyandL11,
author = {Tobias Weyand and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Discovering favorite views of popular places with iconoid shift},
booktitle = {{IEEE} International Conference on Computer Vision, {ICCV} 2011, Barcelona,
Spain, November 6-13, 2011},
pages = {1132--1139},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/iccv/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126361},
doi = {10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126361},
timestamp = {Thu, 19 Jan 2012 18:05:15 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/iccv/WeyandL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Level-Set Person Segmentation and Tracking with Multi-Region Appearance Models and Top-Down Shape Information
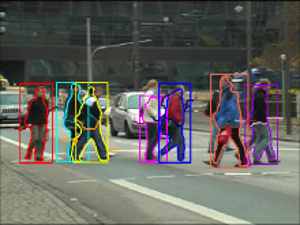
In this paper, we address the problem of segmentationbased tracking of multiple articulated persons. We propose two improvements to current level-set tracking formulations. The first is a localized appearance model that uses additional level-sets in order to enforce a hierarchical subdivision of the object shape into multiple connected regions with distinct appearance models. The second is a novel mechanism to include detailed object shape information in the form of a per-pixel figure/ground probability map obtained from an object detection process. Both contributions are seamlessly integrated into the level-set framework. Together, they considerably improve the accuracy of the tracked segmentations. We experimentally evaluate our proposed approach on two challenging sequences and demonstrate its good performance in practice.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/iccv/HorbertRL11,
author = {Esther Horbert and
Konstantinos Rematas and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Level-set person segmentation and tracking with multi-region appearance
models and top-down shape information},
booktitle = {{IEEE} International Conference on Computer Vision, {ICCV} 2011, Barcelona,
Spain, November 6-13, 2011},
pages = {1871--1878},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/iccv/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126455},
doi = {10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126455},
timestamp = {Thu, 19 Jan 2012 18:05:15 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/iccv/HorbertRL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Fast Image-Based Localization using Direct 2D-to-3D Matching

Estimating the position and orientation of a camera given an image taken by it is an important step in many interesting applications such as tourist navigations, robotics, augmented reality and incremental Structure-from-Motion reconstruction. To do so, we have to find correspondences between structures seen in the image and a 3D representation of the scene. Due to the recent advances in the field of Structure-from-Motion it is now possible to reconstruct large scenes up to the level of an entire city in very little time. We can use these results to enable image-based localization of a camera (and its user) on a large scale. However, when processing such large data, the computation between points in the image and points in the model quickly becomes the bottleneck of the localization pipeline. Therefore, it is extremely important to develop methods that are able to effectively and efficiently handle such large environments and that scale well to even larger scenes.
Multi-Class Image Labeling with Top-Down Segmentation and Generalized Robust P^N Potentials

We propose a novel formulation for the scene labeling problem which is able to combine object detections with pixel-level information in a Conditional Random Field (CRF) framework. Since object detection and multi-class image labeling are mutually informative problems, pixel-wise segmentation can benefit from powerful object detectors and vice versa. The main contribution of the current work lies in the incorporation of topdown object segmentations as generalized robust P N potentials into the CRF formulation. These potentials present a principled manner to convey soft object segmentations into a unified energy minimization framework, enabling joint optimization and thus mutual benefit for both problems. As our results show, the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the categories for which object detections are available. Quantitative and qualitative experiments show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/bmvc/FlorosRL11,
author = {Georgios Floros and
Konstantinos Rematas and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Multi-Class Image Labeling with Top-Down Segmentation and Generalized
Robust {\textdollar}P{\^{}}N{\textdollar} Potentials},
booktitle = {British Machine Vision Conference, {BMVC} 2011, Dundee, UK, August
29 - September 2, 2011. Proceedings},
pages = {1--11},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/bmvc/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.5244/C.25.79},
doi = {10.5244/C.25.79},
timestamp = {Wed, 24 Apr 2013 17:19:07 +0200},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/bmvc/FlorosRL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Real-Time Multi-Person Tracking with Time-Constrained Detection
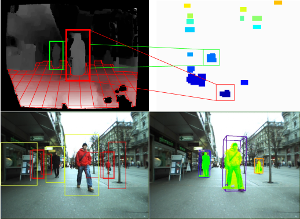
This paper presents a robust real-time multi-person tracking framework for busy street scenes. Tracking-by-detection approaches have recently been successfully applied to this task. However, their run-time is still limited by the computationally expensive object detection component. In this paper, we therefore consider the problem of making best use of an object detector with a fixed and very small time budget. The question we ask is: given a fixed time budget that allows for detector-based verification of k small regions-of-interest (ROIs) in the image, what are the best regions to attend to in order to obtain stable tracking performance? We address this problem by applying a statistical Poisson process model in order to rate the urgency by which individual ROIs should be attended to. These ROIs are initially extracted from a 3D depth-based occupancy map of the scene and are then tracked over time. This allows us to balance the system resources in order to satisfy the twin goals of detecting newly appearing objects, while maintaining the quality of existing object trajectories.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/bmvc/MitzelSL11,
author = {Dennis Mitzel and
Patrick Sudowe and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Real-Time Multi-Person Tracking with Time-Constrained Detection},
booktitle = {British Machine Vision Conference, {BMVC} 2011, Dundee, UK, August
29 - September 2, 2011. Proceedings},
pages = {1--11},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/bmvc/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.5244/C.25.104},
doi = {10.5244/C.25.104},
timestamp = {Wed, 24 Apr 2013 17:19:07 +0200},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/bmvc/MitzelSL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Lying Pose Recognition for Elderly Fall Detection
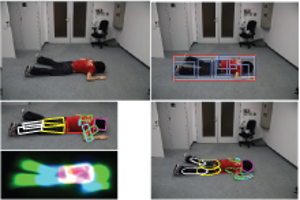
This paper proposes a pipeline for lying pose recognition from single images, which is designed for health-care robots to find fallen people. We firstly detect object bounding boxes by a mixture of viewpoint-specific part based model detectors and later estimate a detailed configuration of body parts on the detected regions by a finer tree-structured model. Moreover, we exploit the information provided by detection to infer a reasonable limb prior for the pose estimation stage. Additional robustness is achieved by integrating a viewpointspecific foreground segmentation into the detection and body pose estimation stages. This step yields a refinement of detection scores and a better color model to initialize pose estimation. We apply our proposed approach to challenging data sets of fallen people in different scenarios. Our quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate that the part-based model significantly outperforms a holistic model based on same feature type for lying pose detection. Moreover, our system offers a reasonable estimation for the body configuration of varying lying poses.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/rss/WangZL11,
author = {Simin Wang and
Salim Zabir and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Lying Pose Recognition for Elderly Fall Detection},
booktitle = {Robotics: Science and Systems VII, University of Southern California,
Los Angeles, CA, USA, June 27-30, 2011},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/rss/2011},
url = {http://www.roboticsproceedings.org/rss07/p44.html},
timestamp = {Sun, 18 Dec 2011 20:27:03 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/rss/WangZL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Online Multi-Person Tracking-by-Detection from a Single, Uncalibrated Camera

In this paper, we address the problem of automatically detecting and tracking a variable number of persons in complex scenes using a monocular, potentially moving, uncalibrated camera. We propose a novel approach for multi-person tracking-bydetection in a particle filtering framework. In addition to final high-confidence detections, our algorithm uses the continuous confidence of pedestrian detectors and online trained, instance-specific classifiers as a graded observation model. Thus, generic object category knowledge is complemented by instance-specific information. The main contribution of this paper is to explore how these unreliable information sources can be used for robust multi-person tracking. The algorithm detects and tracks a large number of dynamically moving persons in complex scenes with occlusions, does not rely on background modeling, requires no camera or ground plane calibration, and only makes use of information from the past. Hence, it imposes very few restrictions and is suitable for online applications. Our experiments show that the method yields good tracking performance in a large variety of highly dynamic scenarios, such as typical surveillance videos, webcam footage, or sports sequences. We demonstrate that our algorithm outperforms other methods that rely on additional information. Furthermore, we analyze the influence of different algorithm components on the robustness.
@article{Breitenstein:2011:OMT:2006854.2007007,
author = {Breitenstein, Michael D. and Reichlin, Fabian and Leibe, Bastian and Koller-Meier, Esther and Van Gool, Luc},
title = {Online Multiperson Tracking-by-Detection from a Single, Uncalibrated Camera},
journal = {IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.},
issue_date = {September 2011},
volume = {33},
number = {9},
month = sep,
year = {2011},
issn = {0162-8828},
pages = {1820--1833},
numpages = {14},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2010.232},
doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2010.232},
acmid = {2007007},
publisher = {IEEE Computer Society},
address = {Washington, DC, USA},
keywords = {Multi-object tracking, tracking-by-detection, detector confidence particle filter, pedestrian detection, particle filtering, sequential Monte Carlo estimation, online learning, detector confidence, surveillance, sports analysis, traffic safety.},
}
Online Loop Closure for Real-time Interactive 3D Scanning

We present a real-time interactive 3D scanning system that allows users to scan complete object geometry by turning the object around in front of a real-time 3D range scanner. The incoming 3D surface patches are registered and integrated into an online 3D point cloud. In contrast to previous systems the online reconstructed 3D model also serves as final result. Registration error accumulation which leads to the well-known loop closure problem is addressed already during the scanning session by distorting the object as rigidly as possible. Scanning errors are removed by explicitly handling outliers based on visibility constraints. Thus, no additional post-processing is required which otherwise might lead to artifacts in the model reconstruction. Both geometry and texture are used for registration which allows for a wide range of objects with different geometric and photometric properties to be scanned. We show the results of our modeling approach on several difficult real-world objects. Qualitative and quantitative results are given for both synthetic and real data demonstrating the importance of online loop closure and outlier handling for model reconstruction. We show that our real-time scanning system has comparable accuracy to offline methods with the additional benefit of immediate feedback and results.
@article{DBLP:journals/cviu/WeiseWLG11,
author = {Thibaut Weise and
Thomas Wismer and
Bastian Leibe and
Luc J. Van Gool},
title = {Online loop closure for real-time interactive 3D scanning},
journal = {Computer Vision and Image Understanding},
volume = {115},
number = {5},
pages = {635--648},
year = {2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2010.11.023},
doi = {10.1016/j.cviu.2010.11.023},
timestamp = {Mon, 18 Apr 2011 08:20:18 +0200},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/journals/cviu/WeiseWLG11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Fast PRISM: Branch and Bound Hough Transform for Object Class Detection
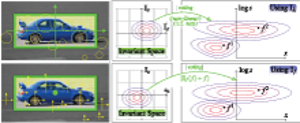
This paper addresses the task of efficient object class detection by means of the Hough transform. This approach has been made popular by the Implicit Shape Model (ISM) and has been adopted many times. Although ISM exhibits robust detection performance, its probabilistic formulation is unsatisfactory. The PRincipled Implicit Shape Model (PRISM) overcomes these problems by interpreting Hough voting as a dual implementation of linear sliding-window detection. It thereby gives a sound justification to the voting procedure and imposes minimal constraints. We demonstrate PRISM’s flexibility by two complementary implementations: a generatively trained Gaussian Mixture Model as well as a discriminatively trained histogram approach. Both systems achieve state-of-the-art performance. Detections are found by gradient-based or branch and bound search, respectively. The latter greatly benefits from PRISM’s feature-centric view. It thereby avoids the unfavorable memory trade-off and any on-line pre-processing of the original Efficient Subwindow Search (ESS). Moreover, our approach takes account of the features’ scale value while ESS does not. Finally, we show how to avoid soft-matching and spatial pyramid descriptors during detection without losing their positive effect. This makes algorithms simpler and faster. Both are possible if the object model is properly regularized and we discuss a modification of SVMs which allows for doing so.
@article{DBLP:journals/ijcv/LehmannLG11,
author = {Alain D. Lehmann and
Bastian Leibe and
Luc J. Van Gool},
title = {Fast {PRISM:} Branch and Bound Hough Transform for Object Class Detection},
journal = {International Journal of Computer Vision},
volume = {94},
number = {2},
pages = {175--197},
year = {2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11263-010-0342-x},
doi = {10.1007/s11263-010-0342-x},
timestamp = {Wed, 19 Feb 2014 09:33:24 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/journals/ijcv/LehmannLG11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Real Time Vision Based Multi-person Tracking for Mobile Robotics and Intelligent Vehicles
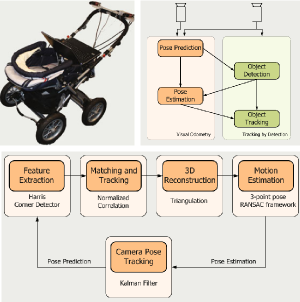
In this paper, we present a real-time vision-based multiperson tracking system working in crowded urban environments. Our approach combines stereo visual odometry estimation, HOG pedestrian detection, and multi-hypothesis tracking-by-detection to a robust tracking framework that runs on a single laptop with a CUDA-enabled graphics card. Through shifting the expensive computations to the GPU and making extensive use of scene geometry constraints we could build up a mobile system that runs with 10Hz. We experimentally demonstrate on several challenging sequences that our approach achieves competitive tracking performance.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/icira/MitzelFSZL11,
author = {Dennis Mitzel and
Georgios Floros and
Patrick Sudowe and
Benito van der Zander and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Real Time Vision Based Multi-person Tracking for Mobile Robotics and
Intelligent Vehicles},
booktitle = {Intelligent Robotics and Applications - 4th International Conference,
{ICIRA} 2011, Aachen, Germany, December 6-8, 2011, Proceedings, Part
{II}},
pages = {105--115},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/icira/2011-2},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25489-5_11},
doi = {10.1007/978-3-642-25489-5_11},
timestamp = {Fri, 02 Dec 2011 12:36:17 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/icira/MitzelFSZL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Efficient Use of Geometric Constraints for Sliding-Window Object Detection in Video

We systematically investigate how geometric constraints can be used for efficient sliding-window object detection. Starting with a general characterization of the space of sliding-window locations that correspond to geometrically valid object detections, we derive a general algorithm for incorporating ground plane constraints directly into the detector computation. Our approach is indifferent to the choice of detection algorithm and can be applied in a wide range of scenarios. In particular, it allows to effortlessly combine multiple different detectors and to automatically compute regions-of-interest for each of them. We demonstrate its potential in a fast CUDA implementation of the HOG detector and show that our algorithm enables a factor 2-4 speed improvement on top of all other optimizations.
Bibtex:
@InProceedings{Sudowe11ICVS,
author = {P. Sudowe and B. Leibe},
title = {{Efficient Use of Geometric Constraints for Sliding-Window Object Detection in Video}},
booktitle = {{International Conference on Computer Vision Systems (ICVS'11)}},
OPTpages = {},
year = {2011},
}
Efficient Object Detection and Segmentation with a Cascaded Hough Forest ISM

Visual pedestrian/car detection is very important for mobile robotics in complex outdoor scenarios. In this paper, we propose two improvements to the popular Hough Forest object detection framework. We show how this framework can be extended to efficiently infer precise probabilistic segmentations for the object hypotheses and how those segmentations can be used to improve the final hypothesis selection. Our approach benefits from the dense sampling of a Hough Forest detector, which results in qualitatively better segmentations than previous voting based methods. We show that, compared to previous approaches, the dense feature sampling necessitates several adaptations to the segmentation framework and propose an improved formulation. In addition, we propose an efficient cascaded voting scheme that significantly reduces the effort of the Hough voting stage without loss in accuracy. We quantitatively evaluate our approach on several challenging sequences, reaching stateof-the-art performance and showing the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/iccvw/RematasL11,
author = {Konstantinos Rematas and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Efficient object detection and segmentation with a cascaded Hough
Forest {ISM}},
booktitle = {{IEEE} International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, {ICCV}
2011 Workshops, Barcelona, Spain, November 6-13, 2011},
pages = {966--973},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/iccvw/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2011.6130356},
doi = {10.1109/ICCVW.2011.6130356},
timestamp = {Fri, 20 Jan 2012 17:21:11 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/iccvw/RematasL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Real-Time Multi-Person Tracking with Detector Assisted Structure Propagation
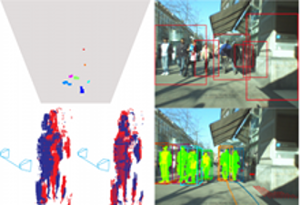
Classical tracking-by-detection approaches require a robust object detector that needs to be executed in each frame. However the detector is typically the most computationally expensive component, especially if more than one object class needs to be detected. In this paper we investigate how the usage of the object detector can be reduced by using stereo range data for following detected objects over time. To this end we propose a hybrid tracking framework consisting of a stereo based ICP (Iterative Closest Point) tracker and a high-level multi-hypothesis tracker. Initiated by a detector response, the ICP tracker follows individual pedestrians over time using just the raw depth information. Its output is then fed into the high-level tracker that is responsible for solving long-term data association and occlusion handling. In addition, we propose to constrain the detector to run only on some small regions of interest (ROIs) that are extracted from a 3D depth based occupancy map of the scene. The ROIs are tracked over time and only newly appearing ROIs are evaluated by the detector. We present experiments on real stereo sequences recorded from a moving camera setup in urban scenarios and show that our proposed approach achieves state of the art performance
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/iccvw/MitzelL11,
author = {Dennis Mitzel and
Bastian Leibe},
title = {Real-time multi-person tracking with detector assisted structure propagation},
booktitle = {{IEEE} International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, {ICCV}
2011 Workshops, Barcelona, Spain, November 6-13, 2011},
pages = {974--981},
year = {2011},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/iccvw/2011},
url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2011.6130357},
doi = {10.1109/ICCVW.2011.6130357},
timestamp = {Fri, 20 Jan 2012 17:21:11 +0100},
biburl = {http://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/bib/conf/iccvw/MitzelL11},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, http://dblp.org}
}
Figure-Ground Segmentation - Object Based

Tracking with a moving camera is a challenging task due to the combined effects of scene activity and egomotion. As there is no longer a static image background from which moving objects can easily be distinguished, dedicated effort must be spent on detecting objects of interest in the input images and on determining their precise extent. In recent years, there has been considerable progress in the development of approaches that apply object detection and class-specific segmentation in order to facilitate tracking under such circumstances (“tracking-by-detection”). In this chapter, we will give an overview of the main concepts and techniques used in such tracking-by-detection systems. In detail, the chapter will present fundamental techniques and current state-of-the-art approaches for performing object detection, for obtaining detailed object segmentations from single images based on top–down and bottom–up cues, and for propagating this information over time.
Visual Object Recognition

The visual recognition problem is central to computer vision research. From robotics to information retrieval, many desired applications demand the ability to identify and localize categories, places, and objects. This tutorial overviews computer vision algorithms for visual object recognition and image classification. We introduce primary representations and learning approaches, with an emphasis on recent advances in the field. The target audience consists of researchers or students working in AI, robotics, or vision who would like to understand what methods and representations are available for these problems. This lecture summarizes what is and isn't possible to do reliably today, and overviews key concepts that could be employed in systems requiring visual categorization.
Table of Contents: Introduction / Overview: Recognition of Specific Objects / Local Features: Detection and Description / Matching Local Features / Geometric Verification of Matched Features / Example Systems: Specific-Object Recognition / Overview: Recognition of Generic Object Categories / Representations for Object Categories / Generic Object Detection: Finding and Scoring Candidates / Learning Generic Object Category Models / Example Systems: Generic Object Recognition / Other Considerations and Current Challenges / Conclusions
Previous Year (2010)

