Publications
Dynamic 3D Scene Analysis from a Moving Vehicle

In this paper, we present a system that integrates fully automatic scene geometry estimation, 2D object detection, 3D localization, trajectory estimation, and tracking for dynamic scene interpretation from a moving vehicle. Our sole input are two video streams from a calibrated stereo rig on top of a car. From these streams, we estimate Structurefrom-Motion (SfM) and scene geometry in real-time. In parallel, we perform multi-view/multi-category object recognition to detect cars and pedestrians in both camera images. Using the SfM self-localization, 2D object detections are converted to 3D observations, which are accumulated in a world coordinate frame. A subsequent tracking module analyzes the resulting 3D observations to find physically plausible spacetime trajectories. Finally, a global optimization criterion takes object-object interactions into account to arrive at accurate 3D localization and trajectory estimates for both cars and pedestrians. We demonstrate the performance of our integrated system on challenging real-world data showing car passages through crowded city areas.
Coupled Detection and Trajectory Estimation for Multi-Object Tracking

We present a novel approach for multi-object tracking which considers object detection and spacetime trajectory estimation as a coupled optimization problem. It is formulated in a hypothesis selection framework and builds upon a state-of-the-art pedestrian detector. At each time instant, it searches for the globally optimal set of spacetime trajectories which provides the best explanation for the current image and for all evidence collected so far, while satisfying the constraints that no two objects may occupy the same physical space, nor explain the same image pixels at any point in time. Successful trajectory hypotheses are fed back to guide object detection in future frames. The optimization procedure is kept efficient through incremental computation and conservative hypothesis pruning. The resulting approach can initialize automatically and track a large and varying number of persons over long periods and through complex scenes with clutter, occlusions, and large-scale background changes. Also, the global optimization framework allows our system to recover from mismatches and temporarily lost tracks. We demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach on several challenging video sequences.
Fast 3D Scanning with Automatic Motion Compensation

We present a novel 3D scanning system combining stereo and active illumination based on phase-shift for robust and accurate scene reconstruction. Stereo overcomes the traditional phase discontinuity problem and allows for the reconstruction of complex scenes containing multiple objects. Due to the sequential recording of three patterns, motion will introduce artifacts in the reconstruction. We develop a closed-form expression for the motion error in order to apply motion compensation on a pixel level. The resulting scanning system can capture accurate depth maps of complex dynamic scenes at 17 fps and can cope with both rigid and deformable objects.
Efficient Mining of Frequent and Distinctive Feature Configurations
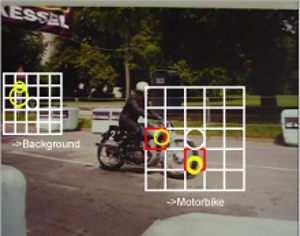
We present a novel approach to automatically find spatial configurations of local features occurring frequently on instances of a given object class, and rarely on the background. The approach is based on computationally effi- cient data mining techniques and can find frequent con- figurations among tens of thousands of candidates within seconds. Based on the mined configurations we develop a method to select features which have high probability of lying on previously unseen instances of the object class. The technique is meant as an intermediate processing layer to filter the large amount of clutter features returned by lowlevel feature extraction, and hence to facilitate the tasks of higher-level processing stages such as object detection.
Depth and Appearance for Mobile Scene Analysis

In this paper, we address the challenging problem of simultaneous pedestrian detection and ground-plane estimation from video while walking through a busy pedestrian zone. Our proposed system integrates robust stereo depth cues, ground-plane estimation, and appearance-based object detection in a principled fashion using a graphical model. Object-object occlusions lead to complex interactions in this model that make an exact solution computationally intractable. We therefore propose a novel iterative approach that first infers scene geometry using Belief Propagation and then resolves interactions between objects using a global optimization procedure. This approach leads to a robust solution in few iterations, while allowing object detection to benefit from geometry estimation and vice versa. We quantitatively evaluate the performance of our proposed approach on several challenging test sequences showing strolls through busy shopping streets. Comparisons to various baseline systems show that it outperforms both a system using no scene geometry and one just relying on Structure-from-Motion without dense stereo
@InProceedings{eth_biwi_00498,
author = {A. Ess and B. Leibe and L. Van Gool},
title = {Depth and Appearance for Mobile Scene Analysis},
booktitle = {International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV'07)},
year = {2007},
month = {October},
keywords = {}
}
Depth-from-Recognition: Inferring Meta-data through Cognitive Feedback

Thanks to recent progress in category-level object recognition, we have now come to a point where these techniques have gained sufficient maturity and accuracy to succesfully feed back their output to other processes. This is what we refer to as cognitive feedback. In this paper, we study one particular form of cognitive feedback, where the ability to recognize objects of a given category is exploited to infer meta-data such as depth cues, 3D points, or object decomposition in images of previously unseen object instances. Our approach builds on the Implicit Shape Model of Leibe and Schiele, and extends it to transfer annotations from training images to test images. Experimental results validate the viability of our approach.
Previous Year (2006)

