Publications
Analyzing Contour and Appearance Based Methods for Object Categorization

Object recognition has reached a level where we can identify a large number of previously seen and known objects. However, the more challenging and important task of categorizing previously unseen objects remains largely unsolved. Traditionally, contour and shape based methods are regarded most adequate for handling the generalization requirements needed for this task. Appearance based methods, on the other hand, have been successful in object identification and detection scenarios. Today little work is done to systematically compare existing methods and characterize their relative capabilities for categorizing objects. In order to compare different methods we present a new database specifically tailored to the task of object categorization. It contains high-resolution color images of 80 objects from 8 different categories, for a total of 3280 images. It is used to analyze the performance of several appearance and contour based methods. The best categorization result is obtained by an appropriate combination of different methods.
On-line Face Tracking Using a Feature-Driven Level Set
An efficient and general framework for the incorporation of statistical prior information, based on a wide variety of detectable point features, into level set based object tracking is presented. Level set evolution is based on the maximisation of a set of likelihoods on mesh values at features, which are located using a stochastic sampling process. This evolution is based on the interpolation of likelihood gradients using kernels centred at the features. Feature detectors implemented are based on moments of colour histogram segmented images and learned image patches located using normalised correlation, although a wide variety of feature detectors could be used. A computationally efficient level set implementation is presented along with a method for the incorporation of a motion model into the scheme.
Interleaved Object Categorization and Segmentation
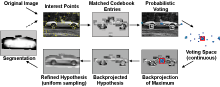
Historically, figure-ground segmentation has been seen as an important and even necessary precursor for object recognition. In that context, segmentation is mostly defined as a data driven, that is bottom-up, process. As for humans object recognition and segmentation are heavily intertwined processes, it has been argued that top-down knowledge from object recognition can and should be used for guiding the segmentation process. In this paper, we present a method for the categorization of unfamiliar objects in difficult real-world scenes. The method generates object hypotheses without prior segmentation that can be used to obtain a category-specific figure-ground segmentation. In particular, the proposed approach uses a probabilistic formulation to incorporate knowledge about the recognized category as well as the supporting information in the image to segment the object from the background. This segmentation can then be used for hypothesis verification, to further improve recognition performance. Experimental results show the capacity of the approach to categorize and segment object categories as diverse as cars and cows.
Previous Year (2002)

